 Botany Botany
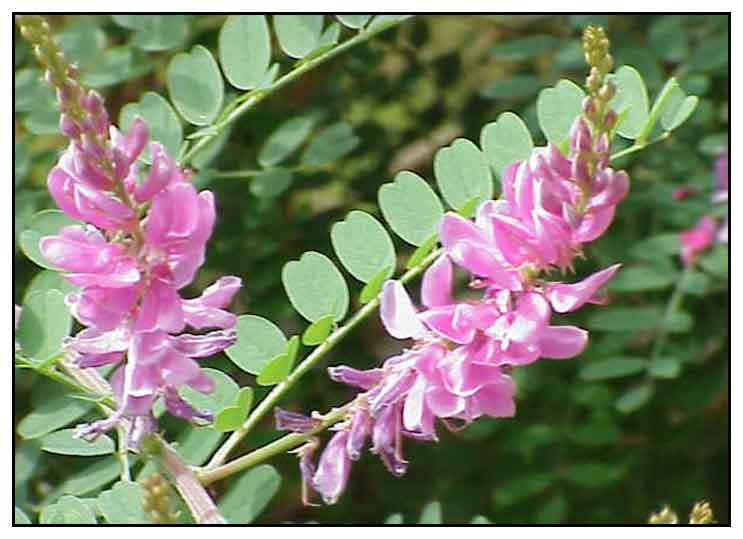
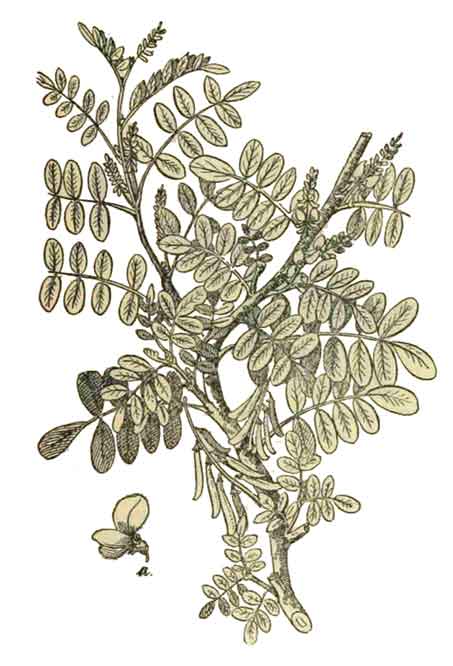
Tina-tinaan is an erect, slightly hairy shrub, 1 to 1.5 meters high. Leaves are 6 to 10 centimeters long, compound, with 9 to 13 leaflets which are obovate-oblong, 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters in length. Flowers are small, reddish or reddish yellow, borne on rather lax racemes 2 to 6 centimeters long. Pods are spreading or reflexed, straight or nearly so, 2 to 3 centimeters long, containing 8 to 12 seeds.
Distribution
- In waste places in and about towns at low and medium altitudes in the Batan Islands and northern Luzon to Mindanao.
- Sometimes cultivated in the Philippines.
- Pantropic.
 Constituents Constituents
- Plant yields a valuable dye, indigo.
- Indican, a glucoside, the oxidized form of Luc indigo or indigo-white, is the product from the fermentation of the fresh green plant.
- Indigotin, or Indigo-blue, an oxidized product that settles at the bottom, is collected, washed, pressed into cakes 3 to 3 1/2 inches square, and finally dried. Yield of indigo is as much as 50 %. Indigotin is insoluble in water, alcohol and dilute acids; soluble in strong sulphuric acid, forming a sulfate of indigo called "extract of indigo." (Q)
- From a complex method of extraction and purification, Indirubin, a pink colored pigment by-product of indigo.
- Phytochemical screening yielded alkaloids, glycosides, carbohydrates, flavanoids, protein and amino acid.
- GC-MS analysis isolated seven phytocompounds
viz. l-(+)-Ascorbic acid 2,6-dihexadecanoate (2.3%), 3-Indoleacetonitrile (14.8%), N-(3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl) Propionyl Piperidin-2-One (14.68%), Methyl stearate (4.27%), 3,6-Diacetyl-9-Ethylcarbazole (47.06%), 5-Hydroxy-L-tryptophan (4.02%) and Tetrachloro-1,2-benzoquinone (12.73%). (see study below) (33)
- Indigo dye contains
flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, glycosides, indigotine, indirubin, rotenoids. (see study below) (34)
Properties
- Plant considered stimulant, alterative, deobstruent, purgative.
- Indigo considered antiseptic and astringent.
- Studies have suggested antioxidant, anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anthelmintic, insecticidal, hypolipidemic, antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anti-leukemic, hepatoprotective, anticancer, immunomodulatory, antiviral properties.s
Parts used
Roots, leaves, roots and juice.
Uses
Folkloric
- Root decoction given for calculus.
- Infusion of root used as antidote for cases of arsenic poisoning.
- Juice of leaves and indigo in powder form have been mixed with honey and used for liver and spleen enlargement, epilepsy and other nervous affections.
- For hydrophobia, two ounces of fresh juice with an equal quantity of milk taken in the morning for 3 days, as prophylactic. In larger doses, the mixture causes purging. Juice is also applied to the part bitten; or the bruised leaves applied as poultice.
- Juice given in asthma, whooping cough, heart palpitations, various lung and renal problems, and edema.
- Leaves and indigo have been used for hepatitis, epilepsy and other nervous conditions.
- Powdered indigo sprinkled on ulcers.
- Used to reduce swellings in the body, relieve bites and stings of venomous insects and reptiles; also used to sooth burns and scalds.
- In Ayurveda, plant used to promote hair growth.
- Decoction of leaves used for bites and stings of venomous insects. Also used to relive pain, burns, and scalds.
- Mixed with castor oil, it is applied to navels of children to promote the action of bowels; mixed with warm water, to the pubes and hypogastrium, and believed to stimulate the bladder for cases of urine retention.
- Chinese used the plant to detoxify the blood and liver, alleviate pains and fever.
- Used for eyeball injury and eyelid inflammation.
- In Nigeria, root decoction applied externally to counteract various poisons.
Others
- Dye: Yields a valuable blue dye, indigo.
- Indirubin: A by-product of indigo, is an active component in the Chinese traditional medicine, Danggui Longgui Wan, used for the treatment of chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML).
Studies
• Hypolipidemic: Study of the chloroform fraction of the alcoholic extract of Indigofera tinctoria showed a significant decrease in plasma triglycerides, total cholesterol, glycerol and free fatty acids accompanied by an increase in HDL. (1)
• Rotenoids / Insecticidal: Indigofera tinctoria is a source of rotenoids, varying according to stages of growth. Rotenone was the most predominant, followed by deguelin, rotenol, sumatrol and dehydrodeguelin. Against the larvae of A stephansi and the adults of C chinensis adults, the insecticidal activity of rotenone, deguelin and dehydrorotenone is much higher than the other rotenoids. (2)
• Status Epilepticus Benefit / Antioxidant: The ethanol extract of Indigofera tinctoria was found to be useful in controlling lithium/pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in albino rats. The extract also exhibited both in-vitro and in-vivo antioxidant activities. (3)
• Antinociceptive: Study showed that Indigofera tinctoria has be peripheral analgesic effect that may be attributed to inhibition of prostaglandin release and other mediators involved. (4)
• Anthelmintic: The methanol extract exhibited maximum anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma, comparable to standard drug Piperazine citrate. (5) Study evaluated the efficacy of Indigofera tinctoria by in vitro and in vivo tests against sheep infected with mixed GI nematodes. An ethanolic extract showed significant (p<0.01) inhibition of egg hatching on in vitro assays and fecal egg count reduction on in vivo testing. (31)
• Antiproliferative Activity: Study showed the flavanoidal fraction of a methanolic extract of the aerial parts of the plant inhibited the proliferation of human Non-Small Cell lung cancer A-549 cells through cell cycle control and apoptosis. Results of its chemopreventive effect suggest a potential for future application in cancer therapy. (6)
• Indirubin / Anti-Tumor / Anti-Leukemia / Anti-Inflammatory: (1) Indirubin has been isolated as a minor constituent of Indigo tinctoria. (2) It is a minor constituent of the traditional Chinese prescription, Dang Gui Long Hui Wan, used in the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). (3) Studies have shown Indirubin inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases in tumor cells. (4) Study have shown anti-inflammatory effects in animals. (5) Meisoindigo, a metabolite of Indirubin, shares similar properties.
• Anti-Tumor / Anti-CDK: Study strongly suggest the inhibition of CDK activity in human tumor cells is a major mechanism by which indirubin derivatives exert potent antitumor efficacy. (9)
• Indirubin / Anti-Breast Cancer: Study showed indirubin has an inhibitory effect on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells growth. Essential factors were incubation time of treatment and indirubin concentration. (7)
• Anti-Diabetic: The methanolic extract of the dried leaves of Indigofera tinctoria showed significant decrease in blood glucose levels in alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. (11)
• Indigtone / Hepatoprotective / Aerial Parts: Fractionation of petroleum ether extract of the aerial parts of IT yielded a bioactive fraction, indigtone which showed significant dose-related hepatoprotective activity against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats and mice. (12)
• Antimicrobial: Indigofera tinctoria showed good antimicrobial activities against all the test microbes (E coli, P aeruginosa, S aureus, B subtilis) at all concentrations. (13)
• Antiseizure: In a PTZ model in albino rats, EITT significantly delayed the onset of convulsions and reduced the duration of seizures in a dose-dependent manner. Increased brain GABA levels suggested a mechanism of facilitated GABAergic transmission. (15)
• Indigtone / Hepatoprotective: Indigtone, a bioactive fraction, showed significant dose-related hepatoprotective activity against CCl4 induced liver injury in rats and mice through a preventive and restorative effect. (16)
• HIV-1 Inhibition: Methanolic extract of whole plants of I. tinctoria showed inhibition of HIV-1 (III B) and HIV-2 (ROD) replication in MT-4 cells. Extracts exhibited EC50 activity of 113 and 125 µg/ml, respectively. (19)
• Hepatoprotective / D-GaIN and CCl4 Toxicity: Study evaluated an Indigofera tinctoria extract against toxicity of D-galactosamine and carbon tetrachloride in situ liver perfusion. Pretreatment with IT in vivo ameliorated D-GaIN and CCl4 induced changes to almost normal state indicating a hepatoprotective effect. (20)
• Antibacterial / Nonmutagenic: Study evaluated an extract of leaves for antibacterial and mutagenic activity. Results showed antibacterial activity, greater than standard linezolid, against clinically important bacterial isolates. Results also showed the extract to be nonmutagenic up to 5 mg/plate in Ames test. (21)
• Antibacterial / Antioxidant / Cytotoxicity / Lung Cancer Cell Line: Leaf extract showed growth inhibition of gram negative bacteria (B. pumilus, S. aureus, Staph pyogenes) with no effect on gram negative bacteria. A strong antioxidant effect was seen, higher than that of ascorbic acid. On cytotoxicity testing on lung cancer cell line NCI-H69, there was decreasing cell viability with increasing concentration. (22)
• Antioxidant / Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents: Study of aqueous extract of I. tinctoria for flavonoid and phenolic content yielded 43.94 µg/mg and 55.05 µg/mg, respectively. DPPH, nitric oxide radical scavenging and OH radical scavenging assays yielded IC50 values of 512.66 ± 1.26 µg/mL, 585.28 ± 1.24 µg/mL, and 483.78 ± 1.18 µg/mL, respectively. Results show potential antioxidant activity associated with high phenolic contents. (24)
• Hepatoprotective / Antioxidant / D-Galactosamine-Endotoxin Induced Acute Hepatitis: Study evaluated the effects of pre-treatment with alcoholic extract of I. tinctoria on liver antioxidant system during acute hepatitis induced by D-GaIN/endotoxin in male albino rats. Pretreatment with Indigofera tinctoria provided considerable antioxidant protection against D-GaIN/endotoxin induced oxidative stress as evidenced by increased activities of all antioxidant enzymes and decreased levels of lipid peroxides. (25)
•
Effect on ß-Amyloid Mediated Alzheimer's Disease in Mice / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study investigated the oxidative reducing effect of methanol extract of Indigo tinctoria leaves on ß-amyloid (25-35) peptide-induced Alzheimer's disease in mice. Reduced antioxidant enzyme levels (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxide and glutathione reductase) in the brain were significantly restored by administration of extract. The extract also moderately prevented the neuronal loss in the hippocampal regions. (26)
• Nephroprotective / Cisplatin Induced Toxicity / Leaves: Study of indigo root and leaves in Cisplatin induced renal damage in Wistar albino rats showed significant dose dependent nephroprotective activity. (27)
• Anti-HIV
Activity: Study screened methanolic extract of whole plants of I. tinctoria for inhibitory activity against HIV-1 (III B) and HIV-2 (ROD) replication in MT-4 cells. Results showed inhibitory activity with EC50 values of 113 and 125 µg/mL, respectively. (28)
• Antihepatotoxic / Paracetamol Induced Toxicity: Study evaluated an aqueous extract of I. tinctoria for antihepatotoxic efficacy against paracetamol induced liver damage in rats. Results showed significant antihepatotoxic effects which may be attributed to flavanoids and the inhibition of lipid peroxidation and enhancement of antioxidant enzyme levels along with free radical scavenging action. (29)
• Immunomodulatory / Leaves: Study evaluated the effects of ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Indigofera tinctoria leaves on in vitro macrophage responses and lymphocyte proliferation isolated from Wistar rats. Evaluation included estimation of NO production, arginase production, lysosomal and phagocytic activities, and analysis of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1ß) production. Collectively, results showed immunostimulating potential evidenced by enhancement of innate and adaptive immune response. (30)
• Indirubin / Antineoplastic Potential / Cancer Cell Lines: Various extracts of Indigofera tinctoria were screened for preliminary cytostatic activity on various cancer cell lines (HCT116, NCI-H460, and U251). Pharmacologic evaluated isolated an antitumor agent, indirubin. A methanolic extract showed potent anticancer activity against all 3 human cell lines. Acute and chronic studies did not show abnormal toxicity at normal doses. In-vitro cytostatic activity of indurubin on 26 cancer cell lines showed potent activity on lung, colon, central nervous system and breast cancer cells. (32)
• Protective Effect on Noise-Induced Behavioral and Biochemical Alterations: Study investigated the protective effect of I. tinctoria on noise induced behavioral and biochemical changes in wistar albino rats. Noise stress can cause free radical damage in immune organs and cause behavioral and biochemical abnormalities. Oral administration of I. tinctoria scavenged noise-induced free radical generation, suggesting an antioxidant property and potential as antistressor. (33)
• Indigo Dye
as Natural Food Colorant / Leaves: Indigo dyes derived from Indigofera tinctoria is a natural blue dye with potential as a natural colorant that reduces the use of synthetic dyes with its carcinogenic impact. Study reports on the analysis of indigo by UV-Vis spectrophotometry and FTIR analysis. The stable blue color of indigo dyes produced by strong UV-Vis showed a maximum absorption peak at wavelength in the visible range of 550-700 nm. (see constituents above) (34)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Constituents
Constituents