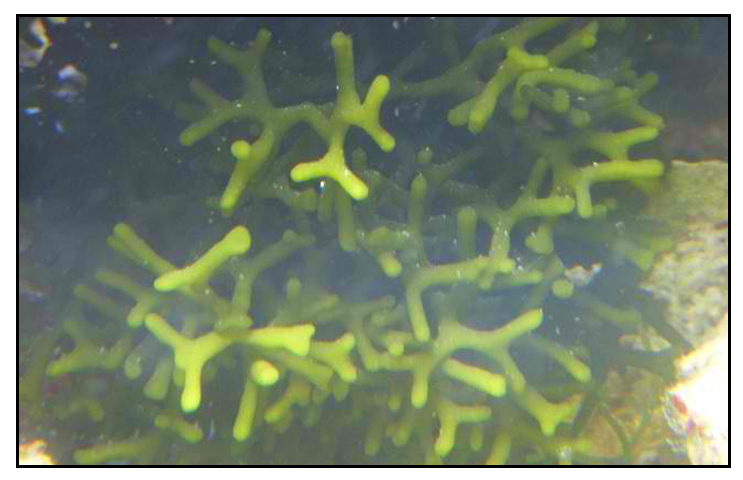
Botany
Pokpoklo is a seaweed with thallus that is generally cylindrical, 3 to 6 millimeters in diameter, and irregularly dichotomously branched, the branches being somewhat compressed at the base. It grows in large, dense, prostrate colonies at a depth of 2 to 3 meters. Most codiums are dioecious and the gametangia are borne laterally on the utricles. (1)
 Distribution Distribution
- Reported on rocky and sandy places in Bangui, Ilocos Norte and La Union provinces, where it is abundant from December to March.
- Also observed in the Bubon Island in Ilocos Norte.
- Also occurs in the north Indian Ocean area.
Constituents
- Study yielded carotenoids constituents: α-carotene, β-carotene, siphonaxanthin and neoxanthin, together with ε-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, astaxanthin, prolycopene like compound, phytofluene like compound, and phytoene like compound. (See study below) (3)
- Yields a considerable amount of iodine, 0.13-0.16% of the dry weight.
(4)
- Study evaluated the nutritional composition of edible green seaweed Codium intricatum. Results showed elemental distribution in the order of Na > K > Ca > Mg _ Fe Mn > Pb > Zn ? Cu > Cd > Cr. Proximate analysis showed high ash and carbohydrate content with estimated values of 37.16 ± 0.21% and 32.16 ± 0.29%, respectively. (see study below) (8)
Properties
- Studies have suggested antibacterial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, fibrinolytic, immunosuppressive, hemagglutination and antimetastatic properties.
Edibility
- Seasonal and edible green algae.
-
Eaten raw after washing, usually mixed with chopped tomatoes and/or green mangoes.
- Popular in the Ilocos region of northern Luzon.
Used as a side dish to fried or grilled meat and fish dishes.
- It is never cooked or blanched as it becomes soft and disintegrates from the heat. In Japan, it is preserved in salt. (5)
- After lato, pokpoklo is considered the next most popular edible seaweed in the Philippines
Folkloric
- No reported folkloric medicinal use in the Philippines.
Studies
• Fibrinolytic Enzymes: Buffer extracts from five species of marine green algae (Codium sp.) were examined for fibrinolytic and protease activities. The C. intricatum extract showed the highest activities in both fibrin plate method and chromogenic assay. Two fibrinolytic enzymes, CIP-I and CIP-II were purified. (2)
• Carotenoids: Besides α-carotene, β-carotene, siphonaxanthin and neoxanthin, the existence of ε-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, astaxanthin, prolycopene like compound, phytofluene like compound, and phytoene like compound was confirmed as the constituents of carotenoids in Codium intricatum. (3)
• Immunosuppressive: Extracts from Liagora sp., Eisenia bicyclis, Sargassum sagamianum, Amphiroa aberrans, Gracilaria verrucosa, Codium fragile, C. intricatum, and C. divaricatum showed pronounced effects on experimental murine skin rejection models suggesting the algae contain bioactive compounds with immunosuppressive activity. (6)
• Screening
of Hemagglutinins in Marine Green Macroalgae: Lectins (hemagglutinins) are widely distributed in nature and play important roles in many biological processes. In a screening study of twelve species of marine green macroalgae from the Java Island coast, Codium intricatum was one of six species that showed strong hemagglutination activity with enzyme-treated rabbit erythrocytes. (7)
• Composition / Antibacterial /Antioxidant: Study evaluated the nutritional composition and antibacterial properties of edible green seaweed Codium intricatum. The methanol extract C. intricatum showed an extended spectrum of inhibitory activity against Gram-positive drug resistant bacterium, Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with MIC and MBC of 250.00 and 500.00 µg/ml, respectively. It was moderately active against Penicillin-acylase producing Bacillus cereus and Listeria monocytogenes, each with MIC of 250 µg/ml. Minimum bactericidal concentration of 1000 µg/ml was observed with the test organisms. There was no inhibitory effect on Gram-negative bacteria. The tested algal extract showed dose dependent radical scavenging activity with EC50 of 40.79 ± 0.015 mg/ GAE/mL, which dose-dependently correlated with phenolic concentration. ( see constituents above) (8)
• Cytotoxic / Anti-Metastatic / Bioactive Polysaccharides: Study evaluated polysaccharide protein fractions from C. intricatum for cytotoxic and inhibitory potential against Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) production. MMPs are novel targets for therapeutic intervention with potential for inhibition of tumor growth, metastasis and invasion. The crude polysaccharides (CPs) and fractions (CFs) yielded carbohydrates, sulfates, protein, ash, lipids, and uronic acid. Both CPs and CFs significantly inhibited growth of breast cancer (MCF-7) in a dose-dependent manner (p<0.05), induced proliferation of HnDFs) and inhibited the production of MMP-1. Results were highly suggestive the the polysaccharide fractions are bioactive molecules with cytotoxic and anti-metastatic potential. (9)
• Siphonaxanthin / Carotenoids produced from Cultivated Seaweed: Floating form cultivation was applied to large-sized edible green alga, Codium intricatum which is uniquely producing a carbonyl carotenoid, siphonaxanthin. This has several anti-disease effects and is also a primal photosynthetic pigment which is found bound to photosynthetic antenna complex usually called siphonaxanthin-chlorophyll protein (SCP). (10)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()





