 Gen info Gen info
- Telosma cordata is a fragrant species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae.
- Clusters of golden yellow blooms along vining stems during summer months, emerging successively over a period of weeks, emitting a rich fragrance during the day and night. (2)
Botany
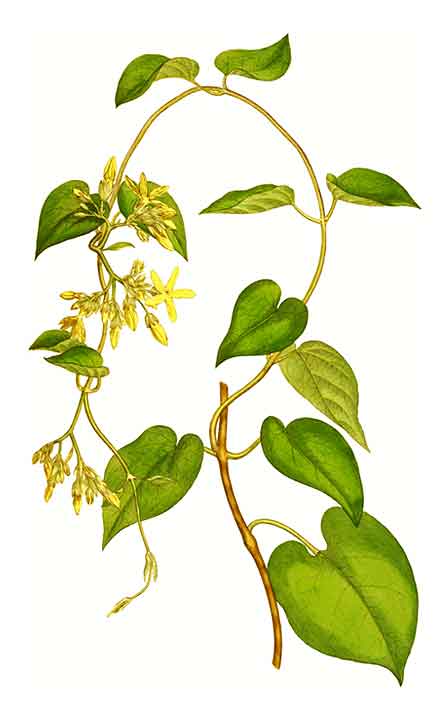
• Stems 1-10 m, yellowish green, pubescent when new, those of previous year pale gray, glabrescent, usually sparsely lenticellate. Petiole 1.5-5 cm; leaf blade ovate, 4-12 × 3-10 cm, base deeply cordate with narrow sinus, apex acuminate; basal veins 3, lateral veins to 6 pairs. Cymes umbel-like, 15-30-flowered; peduncle 0.5-1.5 cm, puberulent. Sepals oblong-lanceolate, puberulent. Corolla yellowish green; tube 6-10 × 4-6 mm, puberulent outside, pilose or glabrous with pilose throat inside; lobes oblong, 6-12 × 3-6 mm, ciliate. Corona lobes slightly fleshy, basal part ovate, apex acuminate, often notched to deeply lobed, internal appendage often longer than lobe proper. Pollinia oblong or reniform. Stigma head capitate. Follicles lanceolate in outline, 7-13 × 2-3.5 cm, glabrous, somewhat obtusely 4-angled. Seeds broadly ovate, ca. 1 × 1 cm, flat, apex truncate, margin membranous; coma 3-4 cm. (Flora of China)
• Telosma cordata is a creeper that can climb as far as 2–5 meters. Vine is small, round and very tough; green and turning to brown on aging. Top covered with dense white bush that can cover other trees completely. Leaves are heart-shaped, growing in pairs. Leaf is about 4–7.5 cm wide and about 6–11 cm long with smooth underside; thin, with clearly veined. The leaf is very thin and clearly veined. Stem is 1.2–2 cm long. Flowers bloom as a bouquet of about 10–20 flowers, greenish yellow, about 1.5 cm diameter, with 5 petals and 5 stamens connected to each other and to the pistils. Flowers are strongly fragrant in the evening. Fruit is smooth, green and round with pointed ends, containing many flat seeds with white fluff attached to the ends. (2)
 Distribution Distribution
- Introduced.
- Cultivated, not naturalized.
- Native to Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, Himalaya, India, Laos, Myanmar, Pakistan, Thailand, Vietnam. (1)
- Cultivated as a floral fragrance plant.
Constituents
- Study of n-hexane extract of leaves isolated four compounds viz., luteine (1), 1-dotriacontanol (2),
24E-stigmasta-5,22-dien-3ß-ol (3), and daucosterol (4). (see study below) (3)
- SDE, GC, and GC-MS analysis of flowers for essential identified 43 compounds.
Geraniol, β-ionone, dihydro-β-ionone, dihydro-β-ionol, and cis- and trans-theaspirane were found to make a major contribution to the characteristic scent of this flower. (5)
- Analysis of methanol extract and various fractions of leaves yielded presence of phenolics, flavonoids, and tannins. (see study below) (6)
- Study of methanol extract of leaves yielded alkaloids, coumarins, tannins, flavonoids, phenols, saponins, anthraquinone. Quantitative analysis yielded total phenolic content 296.10 mg GAE/g, total flavonoid 44.82 mg RE/g, and total tannin content of 309.56 mg GAE/g. (6)
Properties
-
Yellow flowers emit a rich fragrance during the day and night. (2)
-
Studies have suggested antioxidant, anticancer, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, fragrant properties.
Parts used
Flowers, leaves, oil.
Uses
 Edibility Edibility
- Top, fruit, and flowers are edible, consumed as vegetables. The top is believed to be the most nutritious part. Flower used in desserts. (2)
- Flower buds are eaten, stir-fried or boiled.
- Flowers used for herbal tea. (see study below) (3)
- Blossoms are ingredients of Ilokano dishes like pinakbet and dinengdeng.
Folkloric
- Used for fever, poison antidote, tranquilizer, and treatment for back pain.
- Flower oil used for conjunctivitis.
- In Myanmar, tender leaves eaten as medicine for alcohol dependence and mental disorders. (7)
Others
- Ornamental: Flowers used for bouquets and wreaths.
- Cordage: Vines are tough, used for tying.
- Wood:
Used for construction.
- Perfume: Flowers yield perfumed oil.
Studies
• Antioxidant / Cytotoxic Against Cancer Cell Lines / Leaves: Methanol extract of leaves of Telosma cordata showed in vitro cytotoxic activities against HepG2 (heptonema carcinoma), Fl (fibril sarcoma of uterus), and RD (rhabdosarcoma) with ED values of 39.0, 12.6, and 5.6%, respectively. Methanol extract also showed antioxidant activity with SC 52,3% and IC50 56.9 µg/mL. (see constituents above) (3)
• Making of Herbal Tea / Flowers: Study reports on the processing and production of Pakalana dried flower herbal tea using blanching and vacuum drying and pressure and effects on total phenolic content, antioxidant activity, and organoleptic attributes. Results showed best results with pakalana flowers blanched in hot water 95°C for 5 seconds in the presence of citric acid 0.2%, then vacuum dried at 50°C, -0.8 bar for 6 hours for a final moisture content below 10.0% for preservation. The flowers can be utilized as appropriate material for processing a kind of functional food. (4)
• Flowers Fragrance / Flower Essential Oil: SDE, GC, and GC-MS analysis of flowers for essential identified 43 compounds. Geraniol, β-ionone, dihydro-β-ionone, dihydro-β-ionol, and cis- and trans-theaspirane were found to make a major contribution to the characteristic scent of this flower. (5)
• Hepatoprotective / Anti-Inflammatory / Aceclofenac Toxicity / Leaves: Study evaluated the hepatoprotective effect of T. cordata methanol and fractions of leaves on aceclofenac (ACF) instigated oxidative stress in rats. ACF caused declined (p<0.05) in level of antioxidant enzymes and increase in serum liver markers, and histopathological evidence of hepatocyte inflammation and injuries. Extract treatment reduced liver injuries and restored levels of antioxidant enzymes and free radicals towards normal. Antioxidant activity of methanol extract by DPPH assay showed IC50 212.2 µg/ml, and BSA assay with IC50 229.7 µg/ml. Results suggest Tc possess strong antioxidant and ant-inflammatory potential due to presence of polyphenols and has potential as drug against liver injuries. (see constituents above) (6)
• Acute Toxicity Study / Leaves: Acute toxicity study in female rats by OECD guidelines at initial dose of 50 mg/kbw for 14 days, and in male rats at 100, 500, 1000, 1500, and 3000 mg/kg results in no signs of distress, pain, or toxicity. (6)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()




 Distribution
Distribution
