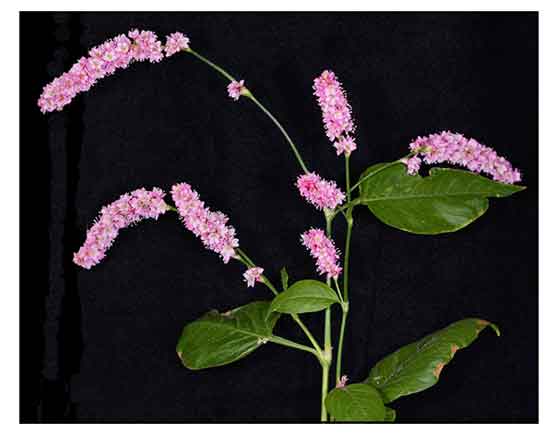
 Gen info Gen info
-
Persicaria orientalis is a species of flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae.
- Plants in the genus are known commonly as knotweeds or smartweeds. As of November 2023, 132 species were accepted,
(24)
- It was initially described as Polygonum orientale by Carl Linnaeus in 1753, and transferred to the genus Persicaria by Edouard Spach in 1841. (23)
- Etymology: Persicaria derives from Latin persica meaning 'peach', alluding to the shape of the leaves. In ancient times a peach was called persike or persica meaning 'Persian apple'. A fruit that reach Europe from China by way of Persia. The species epithet derives from Latin orientalis, meaning 'of or from the East' or 'from the Orient'. (28)
Botany
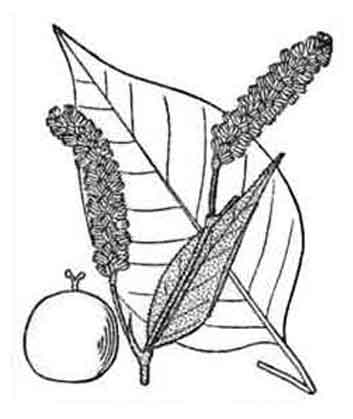
• Polygonum orientale is a branching annual, 30 to 100 centimeters in height. Leaves are long petioled, ovate or ovate-cordate, 15 to 20 centimeters long, 5 to 12 centimeters wide, and covered with soft, silky, gray hairs. Racemes are cylindric, laxly panicled, 8 to 13 centimeters long. Flowers are white. Nut is rounded, black and shining, about 3 millimeters in diameter.
A variety of the plant has rose-pink flowers.
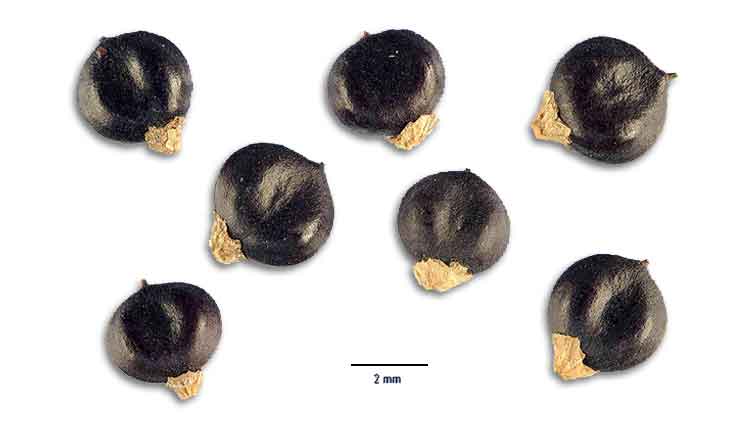 • Habit: Annual, rhizomes, stolons 0. Stem: erect, 50--200(250) cm, +- glabrous to hairy, +- ribbed. Leaf: ocrea funnel-shaped, 10--20(25) mm, brown, papery at base, leaf-like distally, margins truncate, ciliate, bristles 1--3 mm, surface strigose, not gland-dotted; petiole 1--9(14) cm; blade 4--25(30) cm, 2--16 cm wide, ovate, scabrous on midveins, strigose to densely hairy especially along veins, not +- gland-dotted, not dark blotched adaxially, base wedge-shaped, tip acute to acuminate. Inflorescence: axillary, terminal, spike-like, nodding or erect, not interrupted, 20--180 mm, 5--20 mm wide; flowers 1--5; peduncle (0)10--50 mm, glabrous, gland-dotted; bractlets not overlapped; pedicels ascending to spreading, 1--5 mm. Flower: perianth +- bell-shaped, 3--4.5 mm, pink to dark pink, not gland-dotted, lobes 5, obovate, margins of same color, veins +- prominent or not, not anchor-shaped, tips obtuse to rounded; stamens 6--8, included or exserted, anthers pink or red; styles 2, fused basally. Fruit: 2--3.5 mm, 1.5--3 mm wide, lens-shaped, dark brown to black, shiny to dull, minutely rough. (29) • Habit: Annual, rhizomes, stolons 0. Stem: erect, 50--200(250) cm, +- glabrous to hairy, +- ribbed. Leaf: ocrea funnel-shaped, 10--20(25) mm, brown, papery at base, leaf-like distally, margins truncate, ciliate, bristles 1--3 mm, surface strigose, not gland-dotted; petiole 1--9(14) cm; blade 4--25(30) cm, 2--16 cm wide, ovate, scabrous on midveins, strigose to densely hairy especially along veins, not +- gland-dotted, not dark blotched adaxially, base wedge-shaped, tip acute to acuminate. Inflorescence: axillary, terminal, spike-like, nodding or erect, not interrupted, 20--180 mm, 5--20 mm wide; flowers 1--5; peduncle (0)10--50 mm, glabrous, gland-dotted; bractlets not overlapped; pedicels ascending to spreading, 1--5 mm. Flower: perianth +- bell-shaped, 3--4.5 mm, pink to dark pink, not gland-dotted, lobes 5, obovate, margins of same color, veins +- prominent or not, not anchor-shaped, tips obtuse to rounded; stamens 6--8, included or exserted, anthers pink or red; styles 2, fused basally. Fruit: 2--3.5 mm, 1.5--3 mm wide, lens-shaped, dark brown to black, shiny to dull, minutely rough. (29)
Distribution
- Native to the Philippines.
-
In open, wet places along streams at low and medium altitudes in Pampanga and Rizal Provinces in Luzon.
- Also native to Amur, Assam, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China North-Central, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Hainan, India, Jawa, Khabarovsk, Korea, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Manchuria, Myanmar, New Guinea, New South Wales, Northern Territory, Primorye, Queensland, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam, West Himalaya. (16)
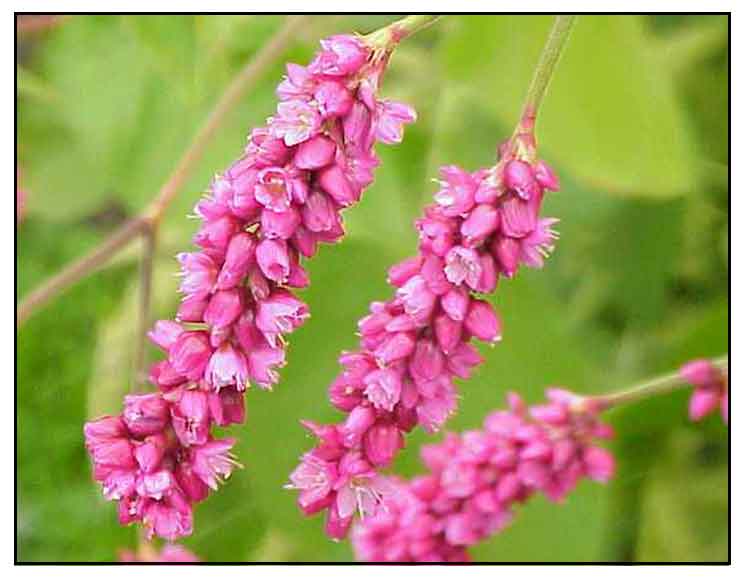 Constituents Constituents
- A total of 153 chemical constituents have been identified from P. orientalis, including flavonoids, carboxylic acids, phenolic acids, amino acids, hydrocarbons, chromones, lignans, volatile oils, amides, and other components. (25)
-
Rootstock yields oxymethyl-anthraquinone, 0.05%.
- Study yielded six compounds: myricitrin, luteolin, gallic acid, catechin, protocatechuic acid and p-hydroxycinnamic acid. (3)
- Study of aerial parts isolated three lignans: arctiin, lappaol B, orientalin.
(5)
- Study of fruits yielded 28-O-ß,7ß-dihydroxt-lup-20(29)-en-28-oate (a new triterpenoid saponin), 5,7-dihydroxychromone, and naringenin.
- Study for chemical constituents yielded seven compounds identified as ombuine-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside (1), ombuine-3-O-rutinoside (2), tryptophan (3), quercetin-3-O-methyl ether (4), kaempferol-3-O-(2"-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl) -beta-D-glucuronopyranoside (5), quercetin-3-O-(2"-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside (6), quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucuronide (7). (12)
- Study for chemical constituents from flowers yielded nine compounds viz. alphitonin (1), methyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (2), apocynin (3), kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucoside (4), 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene (5), 3,3′-dimethoxyellagic-acid-4-O-β-D-glucoside (6), kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside (7), quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside (8), kaempferol (9). (14)
- Ethanolic extract of aerial parts yielded a new anthraquinone glucoside 1-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methyl-6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-anthraquinone (1), along with 1, 6-dihydroxy- 8-methoxy-3-methyl-anthraquinone (2), quercitrin (3), kaempferol-3-O-α-rhamnoside (4), arborinol (5), β-sitosterol (6) and β-sitosterol-D-glucoside (7).
(15)
Properties
- Studies have suggested antioxidant, radical scavenging, cardioprotective, antihyperglycemic, melanogenesis inhibitory, bone healing, phytoremediative, antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory, antidiarrheal, cytotoxic, thrombolytic properties.
Parts used
- Roots, fruit, leaves, whole plant.
 Uses Uses
Folkloric
- Nuts prescribed for flatulence and for tuberculous swellings.
- In India, whole plant is used for whooping cough and menorrhagia. Fruit and leaves are burned and prescribed for fever. Decoction of leaves used for liver and splenic diseases.
(6)
- Decoction of ripe fruits used for treatment of hepatitis.
- In Bangladesh, roots or root juice use for urinary retention, taken to increase frequency of urination.
(20)
- Infusion used as tonic; also used in ulcerative colitis and as remedy of fever. (22)
- In Chinese herbal medicine, used for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, coronary heart disease, hernia, carbuncles, dilated bronchiectasis, as antimicrobial, and to enhance immunity
. (27)
Others
- Herbal tonifying liquid: A constituent of an herbal spleen tonifying and liver protection liquid, together with P. orientalis, Prunella vulgaris, Radix bupleuri, R. rubescens, among others. (21)
Studies
• Taxifolin / Antioxidant: Study showed the taxifolin from Polygonum orientale showed very potent antioxidant activity. (1)
• Free Radical Scavenging: Study investigated the free radical scavenging potentials of P orientale extracts. Results showed the free radical-scavenging activities to be: methanol>ethanol>water>ethyl acetate>chloroform. (2)
• Cardioprotective / Antioxidant / Flowers: Study evaluated the protective effect of flowers, leaves, and main stem of Polygonum orientale on H9c2 myocardial cells oxidative injury induced by H2O2. Results showed a protective effect on H9c2 myocardial cells oxidative injury. The activity showed a positive correlation with antioxidant activities. (4)
• Antihyperglycemic / Flowers: Study evaluated the antihyperglycemic effect of an aqueous extract of flowers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Results showed significant reduction of blood glucose, serum cholesterol, and increase in liver glycogen. (6)
• Cardioprotective Flavonoids: A FEE (flavonoid-enriched extract) was reported to show cardioprotective effect. Study isolated twenty-three active phenolics including ten flavonoid C-glycosides and six flavonoids O-glycosides. (7)
• Bone Healing / Roots: Study showed root tubers of P. orientale could increase ALP activity and DNA synthesis by stimulating proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro, respectively. Results partly explain the pharmacologic ways the herb promotes the healing of bone fractures and rheumatism. (8)
• New Triterpenoid Saponin / Fruits: Study of fruits yielded 28-O-ß,7ß-dihydroxt-lup-20(29)-en-28-oate (a new triterpenoid saponin), 5,7-dihydroxychromone, and naringenin. (9)
• Effects on Osteoblastic Cell Growth / Benefits for Bone Healing and Rheumatism: Study showed root tubers could increase both ALP activity and DNA synthesis by stimulating proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro, with the potential to promote healing of bone fractures and rheumatism. . (10)
• Absorption of Basic Dyes on P. orientale Activated Carbon: Low cost activated carbon from Polygonum orientale was evaluated for its ability to remove basic dyes (malachite green and rhodamine B). Thermodynamic study showed the adsorption was a spontaneous endothermic process. (11)
• Phytoremediation of Phenol from Waste Water: Removing phenol from wastewater is a major challenge of international concern. Study evaluated the ability of P. orientale to phytoremediate phenol. Results provide a theoretical basis for the understanding of mechanisms involved in removal of phenol by P. orientale. (13)
• Antinociceptive / Leaves: Study investigated methanolic extract of Persicaria orientalis leaves for antinociceptive activity in a rodent model using hot plate and tail immersion methods for acute effect and carrageenan-induced paw edema and formalin-induced edema methods for chronic inflammatory effect. Results showed antinociceptive effect and protecting effect against inflammatory stimuli which may be due to phenolic and flavonoid compounds. (18)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Anti-Diarrheal / Thrombolytic / Cytotoxic / Leaves: Study evaluated of methanolic extract of leaves showed significant anti-inflammatory (inhibition of hypotonicity-induced human red blood cell hemolysis and albumin denaturation) and anti-diarrheal (castor oil-induced diarrhea) effects and moderate thrombolytic (33.13% clot lysis) and lower cytotoxic (LC50 58.91 µg/ml in brine shrimp lethality) activities. (19)
• Melanogenesis Inhibition / Phenylpropanoids / Roots: Hyperpigmentation is an important cosmetic issue, and the prominent target for inhibition of hyperpigmentation is tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme in melanogenesis. Study of EtOH extract of roots isolated nine compounds, including five phenyl-propanoid sucrose esters (PSE)(1-5). The PSEs signficantly reduced extracellular melanin formation in B16 melanoma cells and inhibited tyrosinase monophenolase and diphenolase activity in a dose dependent manner. Compound 4 was twice as effective as kojic acid, when L-DOPA was used as substrate. Compounds 1 and 4 showed better inhibitory activity (>59%) on melanin synthesis at concentration of 50 µM compared with arbutin (730 µM). Results suggest the roots is a potential source of natural compounds for dermatological use and cosmetological use research. (26)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Seeds in the cybermarket.
|

![]()




 • Habit: Annual, rhizomes, stolons 0. Stem: erect, 50--200(250) cm, +- glabrous to hairy, +- ribbed. Leaf: ocrea funnel-shaped, 10--20(25) mm, brown, papery at base, leaf-like distally, margins truncate, ciliate, bristles 1--3 mm, surface strigose, not gland-dotted; petiole 1--9(14) cm; blade 4--25(30) cm, 2--16 cm wide, ovate, scabrous on midveins, strigose to densely hairy especially along veins, not +- gland-dotted, not dark blotched adaxially, base wedge-shaped, tip acute to acuminate. Inflorescence: axillary, terminal, spike-like, nodding or erect, not interrupted, 20--180 mm, 5--20 mm wide; flowers 1--5; peduncle (0)10--50 mm, glabrous, gland-dotted; bractlets not overlapped; pedicels ascending to spreading, 1--5 mm. Flower: perianth +- bell-shaped, 3--4.5 mm, pink to dark pink, not gland-dotted, lobes 5, obovate, margins of same color, veins +- prominent or not, not anchor-shaped, tips obtuse to rounded; stamens 6--8, included or exserted, anthers pink or red; styles 2, fused basally. Fruit: 2--3.5 mm, 1.5--3 mm wide, lens-shaped, dark brown to black, shiny to dull, minutely rough. (
• Habit: Annual, rhizomes, stolons 0. Stem: erect, 50--200(250) cm, +- glabrous to hairy, +- ribbed. Leaf: ocrea funnel-shaped, 10--20(25) mm, brown, papery at base, leaf-like distally, margins truncate, ciliate, bristles 1--3 mm, surface strigose, not gland-dotted; petiole 1--9(14) cm; blade 4--25(30) cm, 2--16 cm wide, ovate, scabrous on midveins, strigose to densely hairy especially along veins, not +- gland-dotted, not dark blotched adaxially, base wedge-shaped, tip acute to acuminate. Inflorescence: axillary, terminal, spike-like, nodding or erect, not interrupted, 20--180 mm, 5--20 mm wide; flowers 1--5; peduncle (0)10--50 mm, glabrous, gland-dotted; bractlets not overlapped; pedicels ascending to spreading, 1--5 mm. Flower: perianth +- bell-shaped, 3--4.5 mm, pink to dark pink, not gland-dotted, lobes 5, obovate, margins of same color, veins +- prominent or not, not anchor-shaped, tips obtuse to rounded; stamens 6--8, included or exserted, anthers pink or red; styles 2, fused basally. Fruit: 2--3.5 mm, 1.5--3 mm wide, lens-shaped, dark brown to black, shiny to dull, minutely rough. ( Constituents
Constituents Uses
Uses 