 Botany Botany
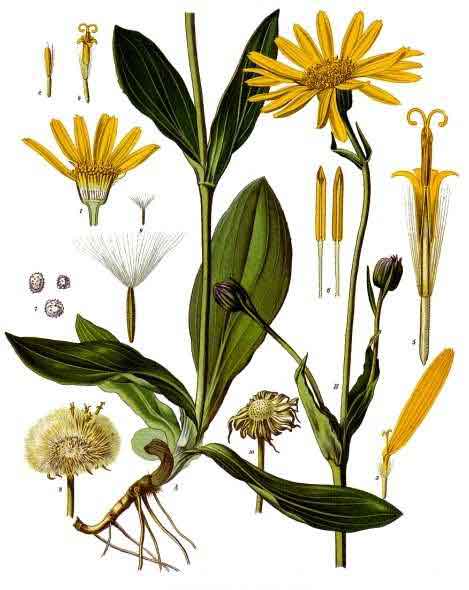
Arnica is a perennial plant growing to a height of 20 to 60 centimeters. Stems are round, slightly hairy, 20 to 60 centimeters, usually supporting a single flower head. Leaves are bright green, oblong-ovate, short-petioled, most in a basal rosette. The upper ones are smaller and sessile, toothed and slightly hairy, while the lower leaves have rounded tips. Flower heads are 8 to 9, large and daisy-like, yellow-orange, about 5 centimeters in diameter. Fruit is brownish, with a single row of white barbed hair.
 Distribution Distribution
- Introduced.
- May be abundant in higher elevations.
Constituents
- Yields traces of non-toxic alkaloids tussilagine and isotussilagine.
- Also yields arnicin (more in the flowers than the rhizomes), a volatile oil (0.3 - 1.0%), thymol (an essential oil), fatty acids, caffeic acid, phytosterols, flavonoids, inulin, carotenoids, resin, tannins, phulin.
- Arnica oil is 50% fatty acids (linolenic, palmitic, linoleic, myristic, etc.) and 50% mixture of thymol, thymol esters, thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether, and phlorol isobutyrate.
- Yields amines (betaine, choline and trimethylamine), carbohydrates (mucilage, polysaccharides including inulin), coumarins (scopoletin and umbelliferone), flavonoids (betuletol, eupafolin, flavonol glucoronides, hispidulin, isorhamnetin, kaempferol, laciniatin, luteolin, patuletin, quercetin, spinacetin, tricin) and terpenoids (sesquiterpene lactones of the pseudoguaianolide-type).
- Study six sample of flower heads yielded four flavonoid aglycones were detected with known compounds - scutellarein-6-methyl ether (hispidulin), scutellarein 6,4’-dimethyl ether (pectolinarigenin), 6-hydroxyluteolin 6-methyl ether and kaempferol 6-methyl ether. (see study below) (27)
Properties
- Bark is bitter and acrid, the smell similar to apples.
- Considered antispasmodic, carminative, diuretic, emollient, expectorant, parasiticide, vulnerary.
- Considered estrogenic, galactagogue, emmenagogue.
Parts used
Flowers, roots.
Uses
Folkloric
- Tinctures or salves used to promote healing of wounds and bruises.
- Used to soothe muscle aches and reduce inflammation.
- Infusion of flowers used to relive stomach and abdominal pains.
- In homeopathy, commonly used as a tincture, or as a base for compresses and poultices.
Others
- Veterinary: In veterinary phytotherapy, used topically for the treatment of tendon, joint and udder inflammations. Also, for cleaning and treatment of skin and mucous membrane wound, eczema and skin inflammations.
- Tobacco: Dried leaves once used as substitute for tobacco. Swiss mountain guides chewed arnica leaves to prevent fatigue. (17)
- Homeopathy: Whole plant used for homeopathic remedy. (17)
 Studies Studies
• Topical Analgesic / Osteoarthritis: A study was done comparing the effects of ibuprofen and arnica gel preparation for symptom relief in osteoarthritis. With the primary endpoints of pain intensity and hand function, results showed the arnica preparation was not inferior to ibuprofen in treating osteoarthritis of the hands. (5)
• Anti-Inflammatory Study / Effect on Histamine-Induced Vascular Permeability: An animal preclinical study was done to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of AM 6cF in acute and chronic inflammation models. In the acute model, no inflammatory inhibition was note with Arnica treatment prior to carrageenan. In the chronic Nystatin-induced edema model, there was reduced inflammation 6 hr after the application of the inflammatory agent. In a histamine-induced model, pretreatment blocked the action of histamine in increasing vascular permeability. (11)
• Inflammatory Process Modulation / Role of Individual Variation: Study concludes proposing two hypotheses: (1) there is no selective modulation of leucocyte subsets by AM 6cH treatment and (2) there is clear interference of individual kinetic variation in vascular events after treatment with AM 6cH. (15)
• Postpartum Bleeding: In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, treatment with homeopathic Arnica montana and Bellis perennis may reduce postpartum blood loss, as compared to placebo. (12)
• Wound Healing: Study concludes that after foot operations, Arnica D4 can be used instead of diclofenac to reduce wound irritation. (13)
• Effects on Post-Laser Treatment Bruises / No Statistical Difference: A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study of 19 patients to evaluate topical arnica's effect on post-treatment bruising after laser treatment for facial telangiectasia. Results showed no significant difference between topical arnica and vehicle in the prevention or resolution of bruising. (6)
• Homeopathic arnica "No better than placebo": A study looked at 3 groups of patients for carpal tunnel surgery receiving high-potency homeopathic arnica tablets, low potency tablets, and placebo. Results showed "no significant difference" in pain, bruising or swelling between the patient groups. (7) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial was done on 64 adults undergoing elective surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome with three parallel arms. Result of the trial did not suggest that homeopathic arnica has an advantage over placebo in reducing postoperative pain, bruising and swelling.
• Multicenter Trial / Osteoarthritis / Safety and Efficacy: An open multicenter trial investigated the safety and efficacy of A. montana fresh plant gel applied twice daily to 79 patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis of the knee. Results conclude topical application of the AM gel for 6 weeks was a safe, well-tolerated, and effective treatment of mild to moderate OA of the knee. (8)
• Postoperative Blepharopasty Ecchymosis: A DB, placebo-controlled, prospective study showed no statistically significant differences among Arnica prescribed or placebo in reducing post-blepharoplasty ecchymosis. (14)
• Post-Surgical Pain and Inflammation: Study evaluated the used of A. montana as homeopathic remedy for the treatment of inflammatory conditions in pain management and postoperative settings. Results showed Arnica montana is more effective than placebo when used for the treatment of several conditions including post-traumatic and postoperative pain, edema, and ecchymosis. However, dosages and preparations used produced substantial differences in clinical outcomes. Evidence suggests AM may represent a valid alternative to NSAIDs, at least when treating some conditions. (19)
• Neuro-Pharmacological and Analgesic Effects: Study evaluated the neuro-pharmacological and analgesic effect of A. montana in mice. Results showed decreased locomotor and exploratory activities in mice at dose of 100 mg/kg, significant (p<0.05) compared with diazepam 2mg/kg. The crude extract also showed potent analgesic activity at 100 mg/kg (p<0.05) with aspirin 300 mg/kg as reference drug. Results suggest significant analgesic and anxiolytic activity. (21)
• No Effect on Mast Cell Populations in Oral Ulcers in Rats: Study investigated the effect of A. montana on mast cells during wound healing of induced oral ulcers in rats. Results sowed A. montana tincture and gel did not change the mast cell populations during wound healing of oral ulcers in rats. Results suggest the anti-inflammatory effects of A. montana were not related to mast cell degranulation. (22)
• Antioxidant / Cytoprotective: Study evaluated A. montana and A. absinthium ethanolic extracts for chemical composition, antioxidant activity and protective effect against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in a mouse fibroblast-like NCTC cell line. Results showed both extracts were rich in flavonoids and phenolic acids, and good antioxidant activity and cytoprotective effect against oxidative. (23)
• Mechanisms of A. montana Effects on Macrophages: Study evaluated the effect of A. montana on human macrophages using human monocytic leukaemia cell line THP-1. Results identified a group of genes that are upregulated by A. montana in macrophages, many of them involved in the processes of connective tissue remodeling and regeneration. (26)
• Flavonoids / Polyphenolics / Antiradical Properties / Flower Heads: Study or six samples of A. montana flower heads showed the best quality in terms of total flavonoids and phenolics, antiradical properties and external flavonoid profiles were obtained when they were collected at full flowering stage. (see constituents above) (27)
Toxicity concerns
- Helenalin: Contains toxin helenalin, poisonous when ingested in large amounts, producing gastroenteritis and GI bleeding, vomiting, shortness of breath, palpitations. and coma in children.
- May also cause contact dermatitis, especially in those sensitized by sesquiterpenes of the helanalin type.
- The German Commission E has approved arnica only for use on the skin for treating superficial injuries, effects of accidents, insect bites. It is considered unsafe for internal use.
- Most studies and available scientific evidence do not support most of the claims about Arnica's effectiveness.
- Advice made not to apply to broken skin, broken skin, and wounds; also to avoid on mucous membranes. Do not use with a history of allergy to sunflowers, marigold, ragweed, and other members of the Asteracea family. Raw or pure arnica herb is considered unsafe by the FDA. (18)
Herb-Drug Interactions / Caution
• Antihypertensives: Arnica may reduce hypotensive effects.
• Anticoagualants / Antiplatelets: Arnica may potentiate the anticoagulant effect of coumarin constituents. This effect has not been documented in humans. (Also see: Herb-Drug Interactions)
• Pregnancy: Avoid during pregnancy because of possible uterine stimulant action.
• Increased Risks of Bleeding and Bruising: Medications that slow blood clotting (aspirin, clopidorgrel, diclofenac, ibuprofen, dalteparin, enoxaparin, heparin, warfarin, among others) may interact with Arnica, and may cause increased changes of bruising and bleeding. (24)
• Study on Coagulation Effect: Study evaluated the effect of homeopathic remedy A. montana 30CH on blood coagulation in vitro. The results showed homeopathic A. montana 30CH had not significant effect on blood coagulation. However, it might still play a vital role in the process of autoregulation by influencing vascular integrity and platelet activity. (25)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
Oil, tinctures, gels, creams and ointments in the cybermarket.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany Distribution
Distribution Studies
Studies 