 Gen info Gen info
- Adiantum is a genus of about 200 species in the family Adiantaceae, extensively distributed worldwide from cool temperate zones to hot tropical zones. About 30 species and 5 varieties are found in China, and half of these species have been used in traditional Chinese medicine. (7)
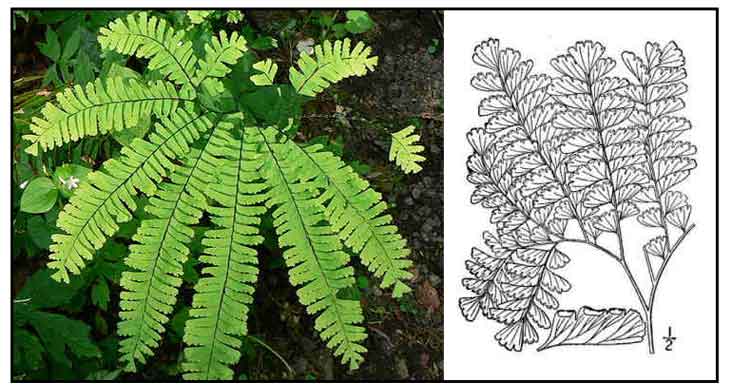
- Adiantum pedatum is a species of fern in the family Pteridaceae, native to moist forests in eastern North America.
The name maidenhair refers to the slender, shining black stipes.
- It was first described by Linnaeus in Species Plantarum in 1753
(the official starting point of modern botanical nomenclature). (11)
- Etymology:
Genus name adiantum comes from the Greek word adiantos, meaning unwetted in reference to the water repellent foliage. Pedatum means 'cut like a bird's foot" in reference to the fronds. (5)
Botany
Adiantum pedatum is a deciduous, clump-forming terrestrial fern growing up to 60 centimeters tall. Stems are wiry, reddish-brown to black. Frond stalks are somewhat frilly, purplish, forked like a fan, with circular or horseshoe shaped rachis. Leaflets are papery and light green.
Distribution
- Recently introduced to the Philippines.
- Native to North America.
Constituents
- Phytochemical screening has of acetone and ethyl acetate extracts yielded terpenoids, cardiac glycosides, steroids, and phenols, with absence of tannin and flavonoids. (see study below) (2)
- Studies for phytoconstituents
yielded isofernane-type (isofernene), isophane and neohopane-type (neohop-12-ene or Neophopene, neohop-13(18)-en-19-a-ol, neohopa-11,13(18)-diene) and norhopane-type (isoglaucanone, glaucanol A, isoadiantone, adiantone, isoadiantol B, adipedatol, and adipedatol Me ether) triterpenoids. Study for fernane type triterpenoids yielded fern-9(11)-ene, 23-hydroxyfernene, fern-7-ene=7-fernene, ferna-7,9(11)-diene, fern-8-ene. (7)
- Studies for chemical constituents have yielded adiantone, adipedatol, caffeic acid, fatty acids, fernene, ferulic acid, filicene, filicinal, iso-fernene, p-coumarin, p-hydrobenzoic acid, protocatechuic acid, sterols, tannin, vanillic acid, and volatile oil. (Singh, 2003) (9)
Properties
- Considered to be anti-rheumatic, astringent, demulcent, emmenagogue, expectorant, febrifuge, haemostatic, pectoral and tonic.
- Study has suggested antibacterial and antioxidant properties.
Parts used
Fronds, stems.
Uses
Edibility
- Fresh fronds used as garnish.
- Dried fronds used in making tea and refreshing fruit juice drink.
Folkloric
- No reported folkloric use in the Philippines.
- Tea or syrup used for nasal congestion, asthma and sore throats.
- Decoction of leaves used to relieve coughing.
- Root decoction used externally to massage into rheumatic joints.
- North Americans chewed the fronds, then applied them to wounds to stop bleeding.
-
Root infusion or decoction rubbed on hands and then to affected area and drunk by Cherokee to treat rheumatism. (6)
- Whole plant infusion used as emetic in agues and fevers.
- Used for bronchitis, whooping cough excessive menses, and dysmenorrhea.
- Plant used as hair conditioner and hair tonic.
- Alcohol leaf extract used topically for thicker hair growth
- Stems used as hair wash to provide shine in the hair.
- In Malaysia, whole plant used for chronic catarrh and other pectoral affections.
- In Chinese traditional medicine, used for relief of fever, to increase urination, remove urinary stones, relief of cough, and to treat diarrhea, hepatitis, hemorrhage, fractures, snakebites, burns and scalds. (7) (8)
Others
- Basketry: Stipe used as ornament in basketry.
- Landscaping: Makes a good ground cover.
Studies
• Antioxidant / Antibacterial: Study of two solvent extracts (acetone and ethyl acetate) showed inhibitory activity against S aureus, K pneumonia, P aeruginosa and E coli, with the acetone extract showing more activity. Study for antioxidant activity by DPPH and FRAP showed Adiantum pedatum to be a potential source of natural antioxidants. (see constituents above) (2)
• Antioxidant / Rhizomes: Studies on scavenging effects on DPPH and ABTS radicals were higher in methanol extracts from rhizomes than those from aerial parts. (Shin, 2009) (10)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Gen info
Gen info