|  Botany Botany
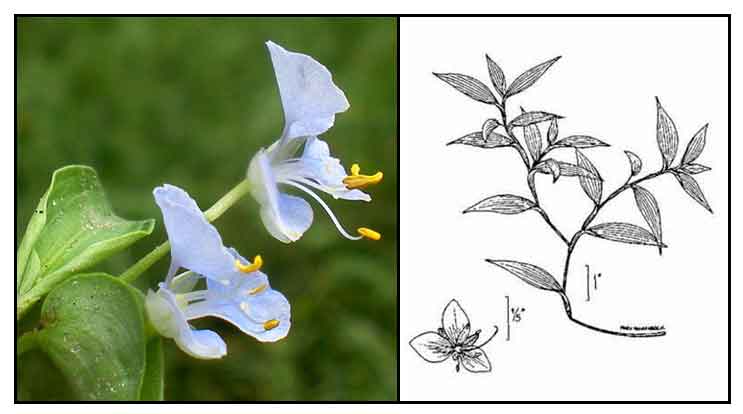
Alikbangon is a mucilaginous,
slender, creeping or ascending branched perennial herb, usually pubescent. Stems
root at the nodes, the ultimate branches ascending. Leaves are green, oblong-lanceolate, 3 to 7 centimeters long, 1 to 2 centimeters wide,
pointed at both ends. Inflorescence is axillary and peduncled. Flowers are cymose, enclosed
in a complicate leaf-like spathe, with free margins. Cymes are usually 2 in each spathe, and are few-flowered.
Inner petals are larger, blue, 6 to 7 millimeters long, and the outer ones much smaller, pale or nearly white.
 Distribution Distribution
- Common throughout
the Philippines in open grasslands and waste places in settled areas
at low and medium altitudes.
- Pantropic.
Constituents
- Study for ascorbic acid and ß-carotene content of leaves on fresh weight basis yielded 7.60 ± 0.48 mg/100g and 3370 ± 0.10 µg/g, respectively. Tannin content was 995.65 ± 25.90 mg/100g.(16)
- In a GC-MS analysis of dried powdered shoots, a methanolic extract showed higher amount of steroids, alkaloids, phenolic compounds tannins, saponins, amino acid and phytosterols, with absence of proteins and anthraquinones.
GC-MS yielded 21 phytoconstituents. The prevailing major components were phenol, 4-ethenyl, acetate (17.90%), n-hexadecanoic acid (1.93%), 9,12-octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester (10.67%), phytol (0.91%), methyl stearate (1.00%), 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid,(Z,Z,Z)- (9.59%), octadecanoic acid (41.49%). (19)
Properties
- Tasteless, cooling
natured.
- Febrifuge, rubefacient, diuretic.
- Good blood coagulant, antifebrile and antidote, tonic for the heart.
- Studies suggest antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, diuretic, anti-inflammatory, wound healing properties.
Parts utilized
Whole plant, latex, leaves, shoots.
Uses
Edibility
- In India young stems are steamed and eaten as vegetables.
- Young leaves used in fresh salads or boiled with butter.
- Small blue flowers and tender flowering tops can be steamed or used as salad green.
Folkloric
· For all kinds
of fever symptoms due to infection: get drug (dried preparation 9 to
15 gms, 30 to 60 gms fresh material) boil to a concentrated decoction
and drink.
· Bruised plant applied to burns, itches and boils.
· Mumps: get fresh plant, crush and squeeze out the juice, then
drink.
· For poisonous snake bites: get fresh plant, crush, squeeze
out the juice, then drink. This drug must be accompanied by an antidote
preparation applied on the bite.
· Used for difficult urination, acute gastroenteritis, erysipelas, laryngopharyngitis, tonsillitis, colds.
· Used for external wound bleeding.
· Used as diuretic.
· Entire plant in decoction is used as an emollient, eye-wash and is also
employed to combat painful discharge of urine.
· Dosage: for 4 to 8, use 30 to 60 gms dried material or 90 to
120 gms fresh material in decoction; pounded fresh material may be applied
externally as a poultice.
· In Africa and Asia, used to treat hypertension, pain and renal diseases.
· In the Gold Coast, the leaves are pounded with the seeds of Leea guineensis and Piper nigrum, made into a poultice and wrapped in a heated plantain leaf and applied to relieve swellings of the groin.
· In Nigeria, taken
as aperient. Decoction used for fevers. Leaf-infusion used as eyewash.
Eye lotion made from plant used for eye complaints. Root decoction used for gonorrhea and dysmenorrhea.
· In Sierra Leone, plant used as wound dressing after circumcision.
· In China, decoction of whole plants used for defervescence and detoxification, for leucorrhea and health protection.
· In Congo leaf-sap used for abscesses, buboes and headache. Leaves believed
to be aphrodisiac.
· Caribbean Indians have used the plant in medicinal baths and as tea to ward off influenza.
· In Mexico used for treatment of conjunctivitis, dermatitis, and dysmenorrhea.
· In Paraguay used for enteritis, gonorrhea and infertility treatments.
· In Hawaii, plant used as blood purifier.
· In India latex, leaf, and shoot used to stop bleeding of wounds and cuts.
· In Ecuador and Peru decoction of tiny blue flowers used as tea for relief of headaches.
· In the Guianas juice from the whole plant used in a decoction against warts. Infusion used against hair loss, fever and biliousness. Juice drunk for high blood pressure. In NW Guyana, used for biliousness, hair loss, kidney disease and for cleansing of the wombs and tubes.
· In Ashanti traditional medicine in Ghana, used as wound healing agent. (2)
· In Santa Lucia, suppository of stem lubricated with castor oil (Ricinus communis) used to help infants move their bowels. (12)
- In Rodrigues Island, Indian Ocean, infusion of leaves of C. diffusa drunk for inflammation; a mixture of leaves of C. diffusa, roots of Coix lacryma and bark of Sida stipulata used for the same. (23)
- The Yao people in Jinping, Yunnan Province of China, drink the decoction of whole plant for defervescence, detoxification, leukorrhea, and health protection. (24)
- In Ghana, used for wound healing in Ashanti traditional medicine. (25)
Others
• Dye: Petal juice used as dye for painting.
• Fodder: In some parts of Africa, India and Asia, used as fodder for small livestock. In Mauritius, contributes to the diet of dairy cows.
Studies
• Antioxidant
/ Antifungal: Commelina diffusa is used as a wound
-healing agent in traditional Ghana medicine. A study on the methanol
extract of Commelina diffusa showed antioxidant and antifungal (against
Trichophyton species) activity confirming its wound healing benefits.
• Antioxidant
/ Antimicrobial / Wound Healing: Study of methanol extracts showed
antimicrobial activity and selective antifungal activity against Trichophyton species. The use of plants for wound healing may be based on antioxidant and antiseptic effects of its constituents. (2)
• Weed as Fodder Crop for Ruminants: Study evaluated the potential of Commelina diffusa as a ruminant food, evaluated in terms of chemical composition and rumen degradation characteristics. Results showed that from a nutritional point of view, C diffusa compares well with many commonly used fodder crops and can be used as a protein source for ruminants on small holder farms. (8)
• Diuretic Activity / Toxicity Study / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the diuretic potential and toxicological profile of aqueous extract from aerial parts of Commelina diffusa. At all doses the aqueous extract produced significant increments in urinary excretion of water and sodium in rats. It also showed a potassium sparing effect. It was devoid of acute toxicity effects. However, in subchronic toxicity study there was a significant increase in water consumption, ALT and total proteins in serum. (11)
• Antimicrobial: Study showed different fractions of C. diffusa produced significant inhibitory against test bacteria and fungi, with a methanolic extract showing the highest inhibition against test bacteria. A diethyl fractions showed highest inhibition against fungi. (13)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study evaluated an ethanolic extract of leaves for anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Results showed significant dose dependent reduction of total foot edema in the Carrageenan induced assay and potent scavenging effect in the DPPH assay. (14)
• Lactogenic / Reproductive Potential / Leaves and Stems: Study evaluated the lactogenic and reproductive potentialities of Commelina diffusa (leaves and stems) and Ficus ingens (leaves) using 24 nulliparous New Zealand white does. Results showed appreciable impact on milk yield and reproductive performance component (litter weight gain). (17)
• Effect of Drying Methods on Antimicrobial Activity / Leaves: Study investigated the effect of different drying methods (sun dry, shade dry, 40˚C oven dry and 60˚ oven dry) on the antimicrobial activities of leaves extract of B. verticillata, C. alata, and Commelina diffusa. Results showed aqueous methanolic crude leaves extract dried via shade-dry and 40˚C oven dry were the most effect methods with retention of most of the bioactive constituents and inhibition of growth of test microbes. (18)
• Cytotoxic / Antimicrobial / Antioxidant: Study evaluated the cytotoxic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities of crude extracts of C. diffusa. An isolated compound, identified as steroid (stigmasterol) showed significant cytotoxic effect on vero cell line. The crude extract and fractions exhibited strong cytotoxicity in brine shrimp lethality bioassay. The crude extract showed strong antibacterial activity against E. coli and strong antioxidant activity using DPPH free radical scavenging assay. (20)
• CNS Depressant Activity: Study evaluated the central nervous system depressant activity of methanolic extract of C. diffusa in mice models using classical models of depression as open field, hole cross forced swimming, tail suspension, and thiopental sodium induced sleeping time in mice. The plant significantly depressed locomotor activity of mice in open field and hole cross tests, and significantly increased immobility time in forced swimming and tail suspension tests, and produced prolongation of sleeping time with thiopental sodium. (21)
• Inhibition of Aluminum Corrosion / Leaves: Study evaluated the effect of C. diffusa leaf extract on corrosion of aluminum in 2M HCl solution using weight loss, thermometric and hydrogen evolution methods. The leaf extract appreciably inhibited the corrosion of aluminum in HCl solution. The inhibition efficiency increased with increase in extract concentration and temperature. (22)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|


![]()

